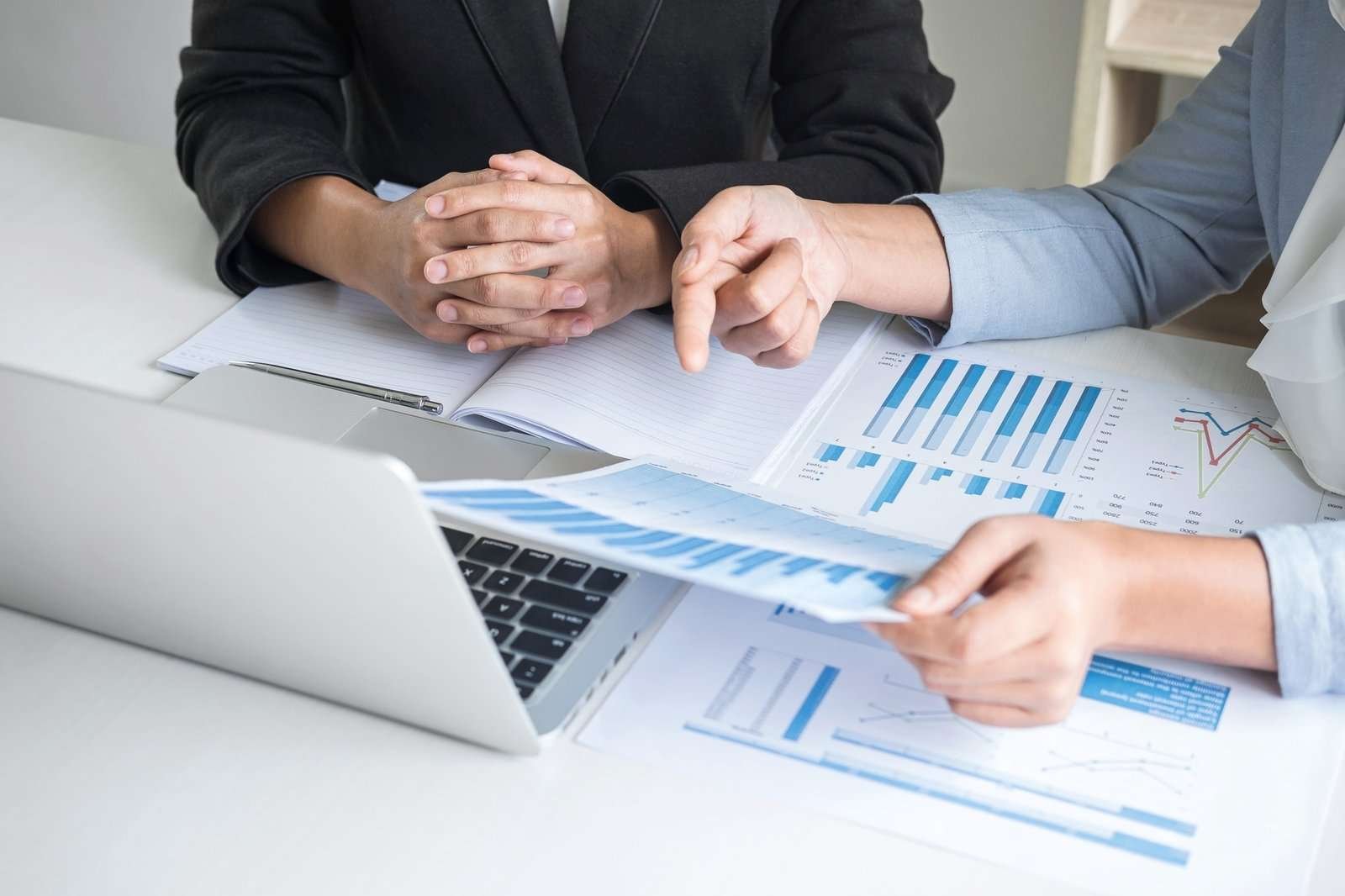
TRA audits are becoming more frequent and data-driven.
Therefore, SMEs must prepare proactively.
Audit readiness protects operations, finances, and reputation.
Moreover, prepared businesses experience fewer disruptions.
As a result, management remains focused on growth.
This guide outlines practical steps for audit readiness.
Understanding TRA Audit Expectations
TRA audits focus on accuracy and consistency.
Therefore, financial records must align with tax filings.
Discrepancies increase audit exposure.
Moreover, TRA reviews VAT, PAYE, SDL, and corporate tax.
Each area requires supporting documentation.
Clear records reduce questioning.
Additionally, digital systems improve TRA audit efficiency.
Authorities detect errors faster.
Prepared SMEs reduce regulatory stress.
Maintaining Accurate Financial Records
Accurate records form the audit foundation.
Therefore, SMEs must record transactions consistently.
Incomplete books raise red flags.
Moreover, proper categorization improves reporting clarity.
Expenses and income must match documentation.
Consistency ensures credibility.
Additionally, supporting documents must remain accessible.
Invoices, receipts, and contracts matter.
Organized records speed audit processes.
Preparing Reliable Financial Statements
Financial statements reflect business integrity.
Therefore, accuracy is essential.
They must align with accounting records.
Moreover, balance sheets show financial position.
Income statements reveal performance trends.
Cash flow statements support liquidity analysis.
Additionally, regular statement reviews prevent surprises.
Errors get corrected early.
Prepared statements build confidence.
VAT and EFD Compliance Best Practices
VAT compliance receives strong TRA attention.
Therefore, SMEs must reconcile VAT regularly.
Mismatch issues trigger audits.
Moreover, EFD machines must function correctly.
Sales data must match VAT returns.
Regular checks prevent penalties.
Additionally, timely VAT filing remains mandatory.
Late submissions attract fines.
Discipline ensures smooth compliance.
Strengthening Internal Controls
Internal controls reduce compliance risks.
Therefore, segregation of duties matters.
It prevents errors and fraud.
Moreover, approval workflows improve accountability.
Transactions require verification.
Control systems enhance accuracy.
Additionally, documented procedures support consistency.
Staff follow clear guidelines.
Strong controls simplify audits.
Managing Audit Risks Proactively
Risk management begins with self-assessment.
Therefore, SMEs should review compliance gaps regularly.
Early action reduces exposure.
Moreover, tax calendars support deadline tracking.
Missed dates cause penalties.
Structured planning improves reliability.
Additionally, professional advisory support adds value.
Experts identify hidden risks.
Guidance strengthens preparedness.
Role of Documentation in Audit Readiness
Documentation validates financial claims.
Therefore, every entry requires evidence.
Missing documents weaken credibility.
Moreover, digital storage improves accessibility.
Records remain secure and retrievable.
Efficient systems save time.
Additionally, retention policies ensure compliance.
Records must meet legal timelines.
Prepared documentation supports audits.
Enhancing Financial Transparency
Transparency builds regulatory trust.
Therefore, clear reporting matters.
Hidden information increases scrutiny.
Moreover, transparent records attract investors.
They support due diligence processes.
Confidence grows with clarity.
Additionally, management gains better insights.
Decisions become data-driven.
Transparency supports growth.
Audit Readiness and Investor Confidence
Investors value compliant businesses.
Therefore, audit readiness increases credibility.
Prepared SMEs attract funding.
Moreover, clean audit histories reduce perceived risk.
They support partnership opportunities.
Trust drives investment decisions.
Additionally, financial discipline reflects strong governance.
It signals long-term sustainability.
Prepared businesses stand out.
Common Audit Mistakes SMEs Should Avoid
Poor record keeping remains common.
Therefore, consistency must improve.
Disorganized books invite audits.
Moreover, delayed tax filings increase risk.
Automation helps prevent delays.
Timeliness remains critical.
Additionally, ignoring professional advice causes issues.
Expert support prevents costly errors.
Guidance protects compliance.
Conclusion: Building a Sustainable Audit-Ready SME
Audit readiness is a continuous process.
Therefore, SMEs must stay disciplined.
Preparation reduces uncertainty.
Moreover, strong systems ensure compliance confidence.
They support transparency and growth.
Well-prepared SMEs operate securely.
This insight empowers Tanzanian SMEs.
It promotes audit readiness and risk reduction.
Preparedness defines long-term success.